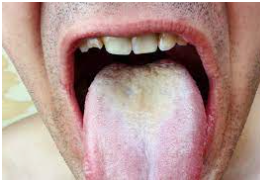
Thrush is indeed a fungal (yeast) illness that could affect one’s mouth, neck, as well as other internal areas. Thrush manifests in one’s mouths as a cottage cheese-like growth — white, elevated sores on one’s tongue as well as cheeks. The disease can rapidly become inflamed, resulting in discomfort and redness inside the mouth.
Thrush is usually characterized by an overabundance of a fungal known as Candida. Oropharyngeal candidiasis seems to be a type of mouth as well as throat thrush.
A thrush infection is inconvenient, but it’s usually a minor issue for healthier people who can get rid of it using antifungal medication within a few weeks.
Is Oral Thrush Contagious?
Would be thrush contagious (passes from individual to individual) but who can acquire it?
While thrush could affect anybody, it is particularly common in babies underneath the age of one month, toddlers, elderly folks, and persons with compromised immune systems (whose symptoms could be more difficult to control). Among the most common diseases amongst HIV/AIDS patients is thrush within the esophagus (swallowing tube).
Thrush is communicable to individuals who are susceptible (like people with weakened immune systems or who are taking certain medications). It’s unlikely for that to be carried on by kissing or even another intimate contact amongst healthy persons. Thrush isn’t extremely contagious throughout most situations, but this can be passed on.
Whether you’re afraid about catching thrush from someone who already has it, stay away from one‘s saliva (spit). Whether you’re near somebody who gets thrush, it’s a good idea to clean your fingers as frequently as possible.
When it Comes to Nursing, How is Oral Thrush a Concern?
Many mothers are concerned about developing or distributing thrush throughout breastfeeding since infants were more vulnerable. That’s a frequent breastfeeding issue, and therapy might be difficult in some situations.
Thrush-infected babies might pass the virus onto their moms. Whenever a baby’s oral infection causes a sore throat and suffering, they scream and become fussy during feeding. Thrush illnesses surrounding the chest as well as nipples can occur amongst mothers (particularly when they’re on antimicrobials) and be passed on to their newborns.
Whenever both the mother and the child acquire thrush, they must be addressed at a similar time to avoid the infection from spreading.
CAUSES As well as SYMPTOMS
What is the cause of thrush?
Candida fungus is found in minute levels throughout most people’s mouths, digestive tracts, and skins. Other microbes and germs inside the body generally keep them within the check. Whenever this equilibrium is disrupted by sickness, stress, even medications, that fungus develops outside of bounds and develops thrush.
Medications that can enable yeast to grow and infect people include:
- Antibiotics.
- Corticosteroids
- Birth control pills.
When you have uncontrolled insulin, you’re more prone to get a Candida infection.
- Infection with HIV.
- Cancer.
- You have a dry mouth.
- Expectant motherhood (caused by the hormonal changes that occur with pregnancy).
- Smoking.
- Dentures that just don’t fit properly.
What do the signs & symptoms of thrush look like?
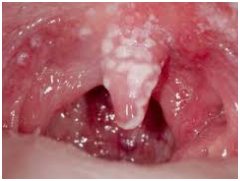
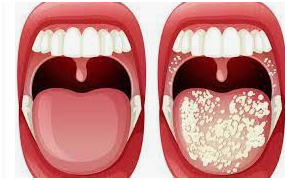
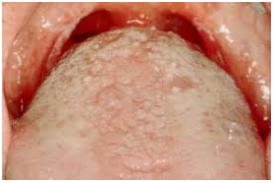
Thrush generally appears out of nowhere. The appearance of buttery white, slightly elevated lesions within your mouth — commonly around your tongues or inside cheeks — is a common indicator. They could also be found on the top of one’s mouth, your jaws, your tonsils, and the bottom of one’s throat. Additional signs and symptoms include:
- Inside and around the edges of one’s mouth, there is redness and pain.
- Taste loss is a condition in which a person’s capacity to taste is lost.
- Within your mouths, you get a cottony sensation.
Whenever you scrape as well as polish your tooth, the lesions could pain and drain a bit. The lesions could develop into your esophagus in extreme situations, causing:
- Suffering from pain or trouble swallowing.
- A sensation of food becoming trapped inside the throat and mid-chest.
- If indeed the infection extends beyond the esophagus, it might cause a fever.
Thrush has the potential to expand to certain other areas of the system, such as the lungs, kidneys, and skins. That’s more common in persons who have cancer, HIV, and other immune-suppressing illnesses.
DIAGNOSTIC ANALYSIS AND TESTS
How do you know if you have thrush?
Whether you had thrush, one’s doctor can typically detect straight away by checking for telltale white sores on one’s mouth, tongues, and checks. When the lesions were lightly brushed away, a reddish, painful patch appears, which might bleed somewhat. Thrush can be diagnosed by examining tissues from such a lesion under a microscope (but a physical exam is not always necessary).
Whereas if thrush has spread to your esophagus, more tests might well be required.
- Throat cultivation may be taken by your healthcare professional (swabbing the back of your throat with sterile cotton and studying the microorganisms under a microscope).
- Another endoscopy examines your esophagus, stomach, including small intestine is recommended (examining the lining of these body areas with a lighted camera mounted on the tip of a tube passed through these areas).
- Examine your esophagus with X-rays.
TREATMENT As well as MANAGEMENT
What is the treatment for thrush?
Thrush could be properly treated in both healthy children and grownups. Those with compromised immune responses, on the other hand, may experience more serious symptoms that are more difficult to cure.
Candida infections could be a sign of a variety of other health issues. Make an appointment with your trusted Odental doctor to check for them and, if necessary, established a treatment regimen.
What can be done to avoid thrush?
You could help yourself avoid thrush by doing the following:
- Maintain healthy oral hygiene habits: Brush one’s teeth times per day plus floss often a day at the very least.
- Avoid mouthwashes and sprays that contain the following ingredients: The regular balance of bacteria in one’s mouth could be disrupted by these items. Consult your dentists or doctors to determine which are suitable to use.
- Visit your dentist regularly: If you possess diabetes and wear prostheses, this is extremely crucial.
Conclusion
Thus thrush is commonly treated with antifungal drugs (such as nystatin). Such medications come in the form of tablets, lozenges, and fluids which are swished about in your mouth before swallowing. These drugs are usually taken for 10 and 14 days. Depending on age as well as the origin of the illness, your medical care professional will devise a unique treatment plan for you.
