The phrase pyorrhea came from the Greek terms pyorrhea, which means “pus discharge.”
Periodontitis, often referred to as pyorrhea, seems to be a complex disease that affects the mouth gums as well as bones. Pyorrhea affects the periodontium (gum complex), which is composed of gingiva, bones, and ligaments, and maintains the tooth. Pyorrhea is indeed a bacterial infection that develops as a consequence of undiagnosed or severe gingivitis.
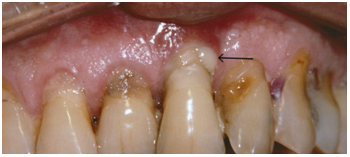
What is Pyorrhea and What are its Varieties?
Pyorrhea comes in a variety of forms, including the following:
- The most prevalent form of pyorrhea includes chronic pyorrhea.
- This is produced via plaque buildup over time, which leads to gum recession as well as bones degradation. Depending on how quickly it is handled, it may get severe or better. Although this kind of Pyorrhea seems more common in adulthood that does not imply that kids remain immune. If tooth hygiene is ignored, children could develop Chronic Pyorrhea.
- Pyorrhea with Aggressive Symptoms:
- Pyorrhea is an inherited condition. If you’ve had Pyorrhea, you’ll want to grab your family tested for it as well, because it’s genetic. Aggressive Pyorrhea gets its name because, if left unchecked, this damaging pyorrhea type may induce rapid bones loss, eventually leading to teeth loss or perhaps a fracture.
- Necrotizing Pyorrhea:
- It is the most serious form of pyorrhea, characterized by the loss of supportive bone, gums tissue, including teeth ligaments due to a loss of blood flow, which leads to serious infection. People with a weakened immune system, such as those who possess HIV or are undergoing cancer treatment, are more likely to develop necrotizing pyorrhoea. Malnutrition plus bad eating habits might also play a role.
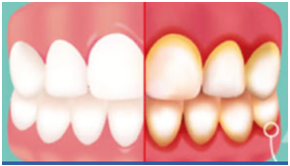
What are Pyorrhea’s indications as well as symptoms?
Pyorrhea develops from gingivitis that begins to manifest serious indications as well as symptoms.
The following are a handful of the most common symptoms:
- Gums that are swollen and puffy.
- Bad breath is a problem.
- Teeth which are loose and gums which bleed easily.
- Chewing is excruciating.
- Around the tooth and indeed the gums, there is pus.
- Gums that are tender and delicate.
- Whenever flossing and brushing, there is bleeding.
- Around the gums as well as the teeth, vast pockets form.
- Gums that retreat, giving the impression that your tooth is longer than they are.
- Whenever eating fruits such as apples, guavas, and other tropical fruits, you may experience bleeding.
Pyorrhea can be caused by a variety of factors
The primary cause is a deficiency of dental cleanliness. Furthermore, because this is a hereditary illness, you may inherit it through your grandparents or family.
The following are among the most common reasons for pyorrhea:
- Unhealthy dental habits:
- Washing and flossing irregularly allows bacteria to proliferate quickly. Flossing is a vital aspect of one’s dental care because it removes plaque and rotten food leftovers from the crevices among your tooth, which are breeding grounds for germs. Pyorrhea occurs when you get comfortable regarding your dental routines to the extent that the covering of bacteria on your tooth hardens into tartar.
- Pyorrhea is produced by the breakdown of such periodontium tissues, which holds the teeth in place against the gums as well as the jawbone. Such tissue is killed by poor dental maintenance. Whereas bacteria cause periodontal diseases, the generation of cytokinesis is indeed an intermediary mechanism that occurs among bacterial activation and tissue death. Periodontal tissue is destroyed when cytokines are present in high concentrations.
- Gingivitis and Periodontal Illness: What’s the Difference? Whenever plaque is not removed, gingivitis develops, which would be the lightest type of periodontal disease. Inflammation with irritation of such gums surrounding the root of the tooth is described as this ailment. Gingivitis can be reversed with proper mouth hygiene and competent dental care. Once gingivitis is not treated, it worsens as well as progress to pyorrhea with periodontitis.
- Diabetes as well as Pyorrhea: Once you have diabetes, one’s chances of getting Pyorrhea increases as well. Patients with diabetes are more prone to have oral problems.
- Vaping: Tobacco usage is among the leading factors of pyorrhea and periodontitis.
Pyorrhea is generally reversible, but it doesn’t imply you should risk it. Although you may possess dental therapy choices to preserve your teeth, keep in mind that if the condition progresses to the stage of no recovery, it may not be possible to retain any or all of them. As a result, we continue to emphasize the importance of maintaining good dental hygiene including seeing your dentists regularly.
How to Prevent Pyorrhea?
Pyorrhea could be avoided in a few ways:
- Flossing, cleaning, plus mouthwash are all recommended.
- Regular Dental Visits – Make an appointment with one’s dentist at least once every six months. It will help throughout diagnosing as well as treating initial signs and side effects, avoiding further complications.
- Scaling – To get rid of tough tartar, stuck food, plus plaque, which are the main causes of bacteria development.
- Root planing smoothes rough tooth surfaces and eliminates germs from beneath the gum line. The dentist would also do a deep cleaning around and beneath the gums to help remove plaques and tartar accumulation throughout the operation.
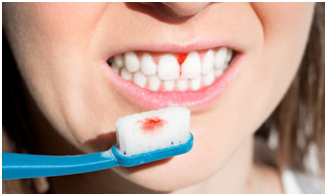
Pyorrhea, whether left untreated, could lead to the bone as well as tissue problems, as well as tooth loss. Aside from tooth losses, the infections could lead to additional health problems.
Pyorrhea could now be treated with laser treatments thanks to recent dental technology breakthroughs, making it significantly simpler to heal in a far less intrusive manner than old surgical techniques, which are highly unpleasant as well as invasive.

Pyorrhea Treatment
Pyorrhea is completely treatable. Plaque removes from the tooth’s surfaces and gums are the most important in-office treatment. Other options for treatment involve:
Maintaining Appropriate Oral Hygiene Activities
All of these are focused on the bacterial colonies that live within the moth.
At Kirkland Superior Dentistry, we offer tips regarding how to maintain one’s teeth as well as gums clean by using toothbrushes and flossing. Additional oral hygiene treatments, such as mouthwash and perhaps a water picker, are also recommended for optimal hygiene.
Antibiotics are drugs that include antibiotics.
Antibiotics may sometimes be used to slow the growth of germs and plaque. Antibiotics can be used topically or orally, or both.
Surgery on the Flaps
When other treatments fail to yield outcomes, one’s periodontist may recommend flap surgery.
Thus the operation aids in the removal of deposits that have accumulated behind the gums. During some circumstances, bone grafting operations might be needed when there is substantial bone loss.
Conclusion
In closing, I would like to say that it is better to get a stitch done in time than wait and get 9 done. Gums problems can also be solved in early stages like other diseases, so better to visit your dentist. Get all the concerned information and select best treatment alternative. You may also contact our clinic for information on 8879348744. Thank you for reading!
