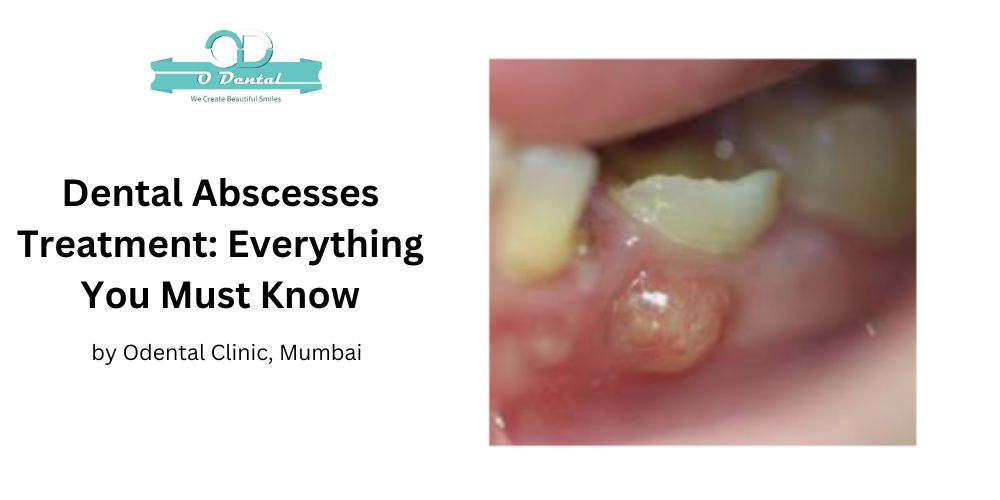
Dental Abscesses Meaning
This dental abscess, also known as a tooth lesion, is a pus-filled infection that develops within the tooth and gums. The abscess is usually caused by a bacterial infection, which has built up inside the tooth’s sensitive pulp. Learn about other bacterial tooth infection pyorrhea and its effects with us.
Plaque, another by of meals, saliva, plus bacteria inside the mouth, contains bacteria that adheres to the tooth and causes harm to them as well as the gums.
The germs may grow within the soft tissues of the teeth or gums when plaque is not eliminated by scrubbing and flossing regularly. The abscess can form as a result of this.
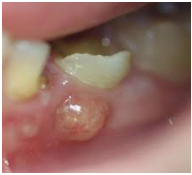
Dental abscesses in a nutshell
- Gingival, periodontal, as well as periapical abscesses are the 3 kinds of dental abscesses.
- Pain, a terrible taste inside the tongue, as well as a fever are all signs of a dental abscess.
- A bacterium infection causes dental abscesses.
- Root tunnel surgery may be required to cure an abscess.
- To reduce pain, eliminate cold drinks and foods and clean with a gentler toothbrush.
Symptoms
Dental abscesses can cause the following signs and symptoms:
- When chewing or contacting the damaged area, you may experience pain.
- Food plus liquids that are cold or hot cause sensitivity.
- a bad taste in one’s mouth
- fever.
- an overall sensation of malaise
- Expanding the mouth is challenging.
- difficulty with swallowing
- insomnia.
Pain remains the most common sign of such a dental abscess. This can be a thumping, excruciating pain. This pain usually begins quickly and intensifies over the next few hrs or days. This pain might radiate towards the ear, jawline, and throat in rare situations.
Types
A dental abscess can be one of 3 kinds:
- Gingival abscess: Such abscess only affects the gum tissues, neither the teeth nor perhaps the periodontal ligaments.
- Periodontal abscess: An periodontal abscess begins inside the tooth’s supporting bones tissue structures.
- Periapical abscesses: this abscess begins inside the tooth’s sensitive pulp.
The severity, as well as location of signs, is determined by the kind of abscess.
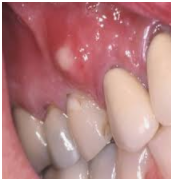
Treatments
Surgery could be required in the case of some abscesses.
Anyone experiencing symptoms related to a dental abscess should consult a dentist as soon as possible. A skilled dentist can readily identify dental abscesses.
People who are having difficulty eating or breathing must go to one‘s local hospital’s emergencies department right away.
If you can’t obtain an appointment with a dentist right away, go to your family doctor.
A doctor could indeed handle an abscess, but individuals could prescribe prescriptions and give advice on consciousness and pain control. They will also know how to get urgent treatment quickly if necessary.
The abscess must be trimmed out and the callus, which includes bacteria, must be depleted. A local anesthetic will be administered by the doctor.
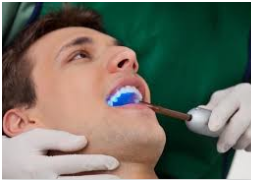
Healing acute periapical abscess: This abscess would be removed through root canals treatment. To allow the abscess to escape, drilling is utilized to create a hole through the dead teeth. This pulp would be cleaned of any damaged tissues. The space is subsequently filled with a root coating to avoid further infections.
A periodontal abscess is treated by draining the abscess as well as cleaning the periodontal pouch. Scaling plus planing underneath the gum lines would then smooth up the edges of the roots of the teeth. This aids in the healing of the teeth and the prevention of additional infections.
Surgery
People who have severe periapical abscesses and a reoccurring infection may require surgical removal of unhealthy tissue.
If you develop periodontal abscesses and persistent infection, you may need your gum tissue altered and your periodontal gap removed. Any oral surgeon would carry out this surgery.
Whenever a dental abscess returns after treatment, the teeth may be removed.
Management of pain
While waiting for therapy, over-the-counter (OTC) medicines may assist to alleviate pain. This is critical to properly follow the instructions on the packaging. Painkillers are just intended to relieve discomfort but are not a substitute for a dental visit.
Effective discomfort relievers include aspirin, ibuprofen, and Tylenol (paracetamol). Several, however, are not appropriate for specific patients (see below):
- Asthma plus ibuprofen Ibuprofen should not be used by asthmatics.
- If you already have or also ever had belly ulcers, avoid using ibuprofen.
- When it comes to children as well as aspirin, there are a few things to consider. Kids under the age of 16 should not take aspirin.
- If you’re pregnant or nursing, avoid using aspirin.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics, in combination with medicines, might well be recommended to stop the infections from developing. Amoxicillin and metronidazole, for example, are antibiotics. Medications should never be used to replace or delay dental care.
Causes of abscess
In most instances, a dental abscess is indeed a consequence of tooth disease. Bacteria, which are commonly found within the plaque, invade and enter a tooth.
Periapical abscess
Bacteria penetrate the teeth through microscopic holes inside the tough outer coating of both the teeth produced by tooth disease and caries. Caries eats away at the dentine, its softer layers of tissue beneath the enamel. Whereas if decay is allowed to progress, the gap will eventually pierce one tooth’s delicate inner tissue by becoming infected.
These are referred to as pulpitis. Even as pulpitis worsens, the germs spread towards the alveolar ridge, which surrounds as well as sustains the teeth, forming a periapical abscess.
Periodontal abscess
Periodontitis is indeed a condition that occurs whenever bacteria found in plaque invade the gums. These gums become inflamed, causing the muscle supporting the tooth’s roots to split from the tooth’s bottom.
Whenever the periodontal membrane breaks off the roots, a periodontal space is developed. The pocket becomes readily soiled and difficult to keep neat. This periodontal abscess develops when germs accumulate inside the periodontal gap.
Conclusion
Thus Periodontal abscesses could occur as a consequence of a dentist operation that results throughout periodontal pockets by accident. This periodontal abscess could also be caused by the usage of medications in unresolved periodontitis, which can hide the signs of an abscess.